Central User Administration in SAP
- How to maintain the user Company address in SAP Author Techrelam. Posted-on 21:48. Maintain Company address for User in SAP.
- AL08 Aktif Kullanıcı Listesi AL11 SAP Dizin Listesi AL12 Display Table Buffer (Exp. Session) AL13 Display Shared Memory (Expert Mode) AL15 Customize SAPOSCOL destination BD54 Maintaining Logical Systems BD64 Maintenance of Distribution Model BSVW Linkage Status Update-Workflow Event CMOD Enhancements DB01 Analyze Exclusive Lockwaits DB02 Tables and Indexes Monitor DB03 Parameter changes in.
- SCUG SAP tcode for – Transfer Users Here we would like to draw your attention to SCUG transaction code in SAP. As we know it is being used in the SAP BC-SEC (Security in Basis) component which is coming under BC module (BASIS).SCUG is a transaction code used for Transfer Users in SAP.
Figure 1: CENTRAL USER ADMINISTRATION
Le maitre de l atlantide poseidon telecharger. Central User Administration best suites an environment where there is
6) Setting the Parameters for Field Distribution Enter Tcode SCUM in central system following screen will appearNow maintain your filed distribution and save it.You can use transaction SUCOMP to administer company address data.You can use transaction SCUG in the central system to perform thesynchronization activities between the central system.
- Complex System Landscape with several clients in different systems (example: ECC, SCM, BI, PI, MDM, SEM, EP)
- Same user works in more than one system (example: User id 1234 in ECC, SCM, BI, PI etc)
- Same user ID should represent the same individual in all the systems (example: User id 1234 belongs XYZ of Finance Dept in Solution manager, ECC, BI, SEM, EP)
- Enormouse efforts required to synchronize user data in all the systems. (example: Assigning a same TCode in all the systems to the same user id)
By implementing Central User Administration we can
- Administer the whole system landscape from one single system
- Overview of overall user data across all the systems
- Additional local maintanence is possible in child systems
The following Data can be distributed in CUA
- User Master Data (example: address, logon data, defaults, parameters)
- Functional Assignment (Profiles, Roles)
- Lock State (lock, unlock)
- Initial Password
Implementing CUA
The following are the steps that are to be performed to activate the CUA in the system landscape
- Setting up the communication user for ALE
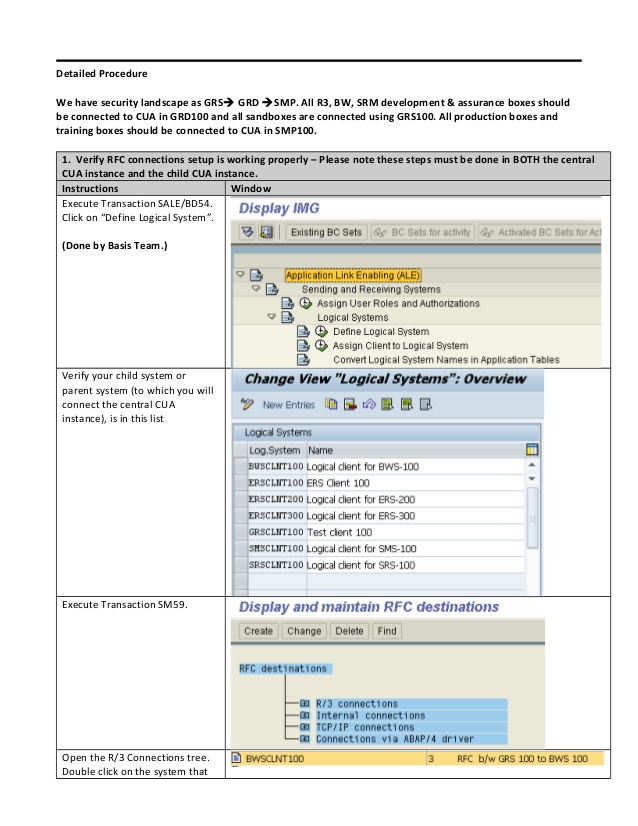
- Define Logical Systems for each client (systems are always refered by logical systems in CUA)
- Assignment of Logical systems to each client
- Define RFC Systems between Central Systems and client systems
- Define ALE Distribution Model
- Switching on Central User Administration
- Define field Attributes
- Migrate Users
Setting up communication user for ALE
Create a user with SU01 in all the systems for ALE communication. The user type is communication user and assign relevant profiles/ roles as per the security policy.
User id in Central System : CUA_sys
Scug Tcode In Sap Security
User id in client System: CUA_sys_client
Define Logical Systems
Transaction SALE -> Define Logical systems
Transaction SALE -> Assign Logical systems to clients
Figure: Creation and Assigning Logical System
Define RFC Destinations
Central System
Transaction SM59 -> create RFC destination from the central system to the client system
Client System
Transaction SM59 -> create RFC destination from the client system to the central system
Figure: Creation of RFC connections
Creation of a Distribution Model for CUA
Central System
Call transaction SCUA -> and give a name to the distribution model (example CUA) and create.

Figure: Name of the distribution model for CUA
Maintain the System Landscape in the next screen.
Figure: System Landscape maintanence in CUA
Maintenance of the Distribution Model for ALE data transfer
Inorder to exchange data with the created distribution model we need to assign BAPIs to the distribution model.
Two types of data can be exchanged between the systems.
User master data (including profiles and roles)
Company Address
List Of Tcodes In Sap
Go to transaction code BD64 -> and create a distribution model (example CUA)
RSUSR_SYS_LIC
Select the distribution model (CUA) -> click on ADD BAPI -> enter the sender and receiver systems -> In the object name/interface field, select USER (R3 system user) and in the Method, select CLONE and save the entries
Figure: Assigning BAPIs to the distribution model
Generating Partner Profiles
In transaction BD64 -> select Environment and click on Generate partner profiles -> select the distribution model you have created earlier and select the partner system (logical system of the client system) and click on execute.
Figure: Generating Partner profiles
Migrating User Data to the client systems
SCUA
Call Transaction SCUG -> select the user and client on transfer users.
See Full List On Sap-tcodes.org
Log Display
To check log for CUA call transaction SCUL
